Wegener's Hypothesis Of Continental Drift
In this article we will discuss virtually:- one. Aim of the Continental Drift Theory 2. Bones Premise of the Continental Drift Theory 3. Evidences iv. Process 5. Evaluation.
Contents:
- Aim of the Continental Drift Theory
- Basic Premise of the Continental Drift Theory
- Evidences in Support of the Continental Drift Theory
- Process of the Continental Drift Theory
- Evaluation of the Continental Drift Theory
one. Aim of the Continental Drift Theory :
Professor Alfred Wegener of Federal republic of germany was primarily a meteorologist. He propounded his concept on continental drift in the year 1912 but it could not come in low-cal till 1922 when he elaborated his concept in a volume entitled 'Die Entstechung der Kontinente and Ozeane' and his book was translated in English in 1924.
Wegener's displacement hypothesis was based on the works and findings of a host of scientists such every bit geologists, palaeo-climatologists, palaeontologists, geophysicists and others.
The main problem before Wegener, which needed caption, was related to climatic changes. It may be pointed out that in that location are ample evidences which indicate widespread climatic changes throughout the past history of the earth. In fact, the continental migrate theory of Wegener 'grew out of the need of explaining the major variations of climate in the past'.
The climatic changes which take occurred on the globe may exist explained in ii means:
(1) If the continents remained stationary at their places throughout geological history of the globe, the climatic zones might have shifted from one region to some other region and thus a particular region might have experienced varying climatic weather condition from fourth dimension to time.
(2) If the climatic zones remained stationary the land masses might have been displaced and drifted.
Wegener opted for the second alternative as he rejected the view of the permanency of continents and ocean basins. Thus, the main objective of Wegener backside his 'displacement hypothesis' was to explain the global climatic changes which are reported to have taken identify during the past world history.
2. Basic Premise of the Continental Drift Theory:
Following Edward Suess, Wegener believed in three layers system of the earth e.g., outer layer of 'sial', intermediate layer of 'sima' and the lower layer of 'nife'. According to Wegener sial was considered to be limited to the continental masses solitary whereas the ocean crust was represented by upper part of sima. Continents or sialic masses were floating on sima without any resistance offered past sima.
He assumed, on the footing of evidences of palaeo-climatology, palaeontology, paleobotany, geology and geophysics, that all the landmasses were united together in the form of ane landmass, which he named Pangaea, in carboniferous period. There were several smaller inland seas scattered over the Pangaea which was surrounded by a huge water trunk, which was named by Wegener as 'Panthalasa', representing primeval Pacific Ocean.
Lauratia consisting of present Northward America, Europe and Asia formed northern part of the Pangaea while Gondwanaland consisting of Due south America, Africa Madagascar (now Malagasy), Peninsular Republic of india, Australia and Antarctica represented the southern part of the Pangaea. Southward Pole was located near present Durban (near Natal in southern Africa) during carboniferous period.
Thus, Wegener'southward theory of continental migrate begins from carboniferous period, he does non describe the weather condition during pre-carboniferous times but the postulation of a carboniferous Pangaea does not hateful that he disbelieves in pre-carboniferous drift: events earlier this time are known with much less certainty, and the distribution of plants and animals can largely be explained past movements which have taken place since the carboniferous'.
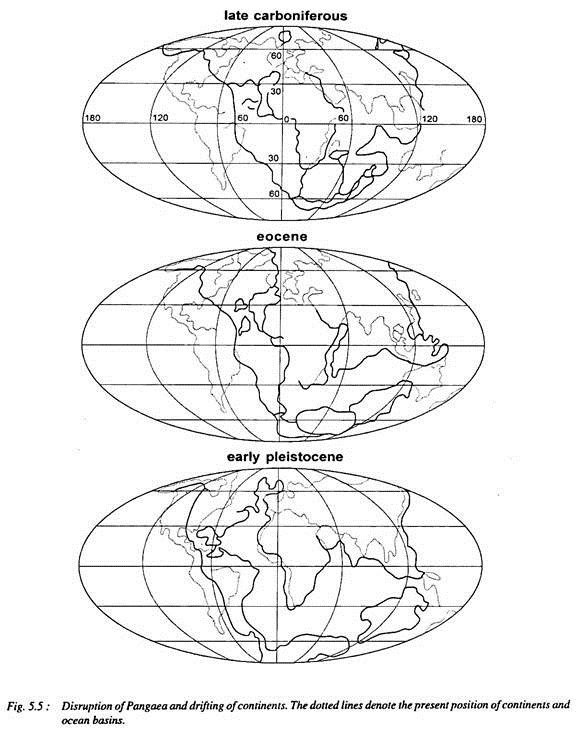
The Pangaea was disrupted during subsequent periods and cleaved landmasses drifted away from each other and thus the present position of the continents and sea basins became possible.
3. Evidences in Support of the Continental Drift Theory :
Wegener has successfully attempted to show the unification of all landmasses in the class of a unmarried Iandmass, the Pangaea, during carboniferous menses, on the ground of evidences gathered from geological, climatic and floral records. He claimed that all the present-day continents could be joined to grade Pangaea.
The following evidences support the concept of the existence of Pangaea during carboniferous menstruum:
(i) According to Wegener there is geographical similarity along both the coasts of the Atlantic Body of water. Both the opposing coasts of the Atlantic can exist fitted together in the same way every bit 2 cut off pieces of forest can be refitted (jig-saw fit) (fig. v.3).

(2) Geological evidences announce that the Caledonian and Hercynian mountain systems of the western and eastern littoral areas of the Atlantic are like and identical (fig. five.4). The Applachians of the northwardeastern regions of North America are uniform with the mountain systems of Ireland, Wales and northwestern Europe.
(3) Geologically, both the coasts of the Atlantic are also identical. Du Toit, after detailed study of the eastern coasts of South America and western coast of Africa, has said that the geological structures of both the coasts are more or less similar. According to Du Toit both the landmasses (i.e., South America and Africa) cannot be really brought together but nearly to each other considering a gap of 400-800 km would separate them due to the existence of continental shelves and slopes of these ii landmasses.
(4) There is marked similarity in the fossils and vegetation remains institute on the eastern declension of South America and the western coast of Africa.
(5) It has been reported from geodetic evidences that Greenland is globe-trotting westward at the charge per unit of 20 cm per year. The evidences of seafloor spreading after 1960 take confirmed the movement of landmasses with respect to each other.
(6) The lemmings (pocket-sized sized animals) of the northern office of Scandinavia have a tendency to run due west when their population is enormously increased only they are foundered in the bounding main water due to absence of whatever land beyond Norwagian declension. This behaviour of lemmings proves the fact that the land- masses were united in the ancient times and the animals used to migrate to far off places in the western direction.
(seven) The distribution of glossopteris flora in India, South Africa, Commonwealth of australia, Antarctica, Falkland islands etc. proves the fact that all the landmasses were previously united and contiguous in the class of Pangaea.
(8) The evidences of carboniferous glaciation of Brazil, Falkland, Due south Africa, Peninsular India, Australia and Antarctica farther prove the unification of all landmasses in one landmass (Pangaea) during carboniferous menses.
4. Procedure of the Continental Drift Theory :
Equally stated earlier the main aim of Wegener behind the postulation of his 'migrate theory' was to explain major climatic changes which are reported to take taken place in the by geological history of the earth, such every bit carboniferous glaciation of major parts of the Gondwanaland. Besides, Wegener also attempted to solve other problems of the globe east.yard., origin of mountains, isle arcs and festoons, origin and evolution of continents and ocean basins etc.
(ane) Force responsible for the migrate:
According to Wegener the continents later breaking away from the Panagaea moved (drifted) in ii directions east.g.:
(i) Equatorward movement and
(two) W movement.
The equatorward movement of sialic blocks (continental blocks) was caused by gravitational differential forcefulness and force of buoyancy. As already stated the continental blocks, according to Wegener, were formed of lighter sialic materials (silica and aluminium) and were floating without any friction on relatively denser 'sima'.
Thus, the equatorward move of the sialic blocks (continental blocks) would depend on the relation of the centre of gravity and the center of buoyancy of the floating continental mass. By and large, these two types of forces operate in opposite directions. 'But because of the oblong form of the earth, these forces are not in straight opposition, simply are then related that, if the buoyancy bespeak lies nether the centre of gravity, the resultant (force) is directed toward the equator'.
The westward movement of the continents was caused by the tidal forcefulness of the sun and the moon. According to Wegener the attractional force of the sunday and the moon, which was maximum when the moon was nearest to the earth, dragged the outer sialic curst (continental blocks) over the interior of the earth, towards the west. Information technology may exist pointed out that in any migrate theory the weakest point and the most difficult problem is related to the competent forcefulness responsible for the motility of the continents.
'Such a force (tidal force/attractional force of the sun and the moon) is extraordinarily small, but, equally in the instance of other forces, the question of time is all important: given sufficient time, it is claimed that even these very pocket-size forces are able to cause movements'.
(2) Actual drifting of the continents:
The disruption, rifting and ultimately drifting of the continental blocks began in carboniferous period. The move of the continental blocks away from the poles was dramatically called by Wegener every bit 'the flight from the poles'. Pangaea was cleaved into two parts due to differential gravitational force and the force of beaconancy. The northern part became Lauratia (Angaraland) while the southern function was chosen by Wegener as Gondwanaland.
The intervening space between these two behemothic continental blocks was filled up with h2o and the resultant water body was called Tethys Sea. This phase of the disruption of Pangaea is called 'opening of tethys'. Gondwanaland was disrupted during cretaceous menses and Indian peninsula, Madagascar, Commonwealth of australia and Antarctica broke abroad from Pangaea and drifted apart nether the impact of tidal forcefulness of the sunday and the moon. North America bankrupt away from Angaraland and drifted westward due to tidal force.
Similarly, South America broke away from Africa and moved westward under the impact of tidal force. Due to northward move of Indian Peninsula Indian Ocean was formed while the Atlantic Body of water was formed due to w motion of two Americas.
It may exist mentioned that Due north and South Americas were drifting westward at dissimilar rates and hence 'S' shape of the Atlantic Ocean could be possible Arctic and North Sea were formed due to flight of the continental blocks from north pole.
The size of the panthalasa (primitive Pacific Sea) was remarkably reduced because of the movement of continental blocks from all sides towards Panthalasa. Thus, the remaining portion of Panthalasa became the Pacific Ocean. Information technology may exist mentioned that disruption, rifting and displacement (drifting) of continental blocks continued from carboniferous period to pliocene period when the present pattern and arrangement of the continents and sea basins was attained (fig. 5.5). There accept been frequent changes in the positions of the equator and the poles as given in table five.one.
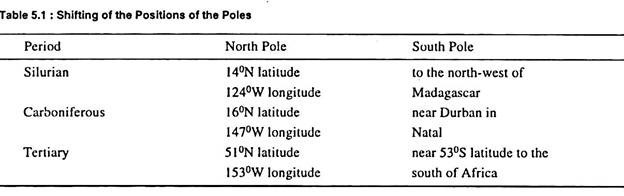
Equator was located at the well-nigh northerly location during Silurian menstruation as it passed north of Norway. Information technology passed through London during carboniferous period and through present locations of the European Tall mountains during tertiary period (fig. v.half dozen.). 'The south pole and equator patently moved into accordant positions. The prevailing westward and equator ward motility must exist referred to these positions'.

(iii) Mountain building:
A.G. Wegener also attempted to solve the problem of the origin of folded mountains of 3rd period on the basis of his continental drift theory. The frontal edges of westward drifting continental blocks of N and South Americas were crumpled and folded against the resistance of the rocks of the sea-flooring (sima) and thus the western Cordilleras of the two Americas (e.g. Rockies and Andes and other mountain bondage associated with them) were formed.
Similarly, the Alpine ranges of Eurasia were folded due to equator ward motility of Eurasia and Africa together with Peninsular India (equator was passing through Tethys body of water at that time). Hither, Wegener postulated contrasting viewpoints. According to Wegener sial (continental blocks) was floating upon sima without whatsoever friction and resistance but during the latter part of his theory he pointed out that mountains were formed at the frontal edges of floating and drifting continental blocks (sialic crust) due to friction and resistance offered by sima.
How could it be possible? The question remains unanswered. Inspite of this serious flaw in the continental drift theory of Wegener, S.W. Wooldridge and R.Southward. Morgan have remarked, 'certainly the trouble of mountain building is one in which the hypothesis of continental drift solves more difficulties than it creates.'
(4) Origin of isle arcs:
Wegener has related the process of the origin of island arcs and festoons (of eastern Asia, West Indies and the arc of the southern Antilles betwixt Tierra del Fugo and Antarctica) to the differential rates of continental drift. When the Asiatic cake (role of Angaraland) was moving westward, the eastern margin of this block could not keep pace with the westward moving major landmass, rather lagged behind, consequently the island arcs and festoons consisting of Sakhalin, Kurile, Japan, Phillippines etc. were formed. Similarly, some portions of North and South Americas, while they were moving westward, were left backside and the island arcs of West Indies and southern Antilles were formed.
(v) Carboniferous glaciation:
There are ample evidences to demonstrate that at that place was large-calibration glaciation during carboniferous period when Brazil, Falkland, Southern Africa, Peninsular Republic of india, Commonwealth of australia, Antarctica etc. were extensively glaciated. Co-ordinate to Wegener all the continental blocks were united together in the class of 1 state mass called as Pangaea.
Southward Pole was located near the present position of Durban in Natal. Thus, South Pole was located in the middle of Pangaea. Consequently, water ice sheets might have spread from South Pole outward at the time of glaciation and the aforesaid land areas, which were closer to South Pole, might take been covered with thick ice sheets.
At much afterwards engagement, these land areas might have parted away due to disruption of Pangaea and related continental drift. Glossopteris flora might accept too been distributed over the aforesaid areas when these were united together.
v. Evaluation of the Continental Drift Theory:
It may be pointed out that Wegener's continental drift theory widely departed from the contemporary orthodox geological ideas of the nineteenth century and the time-honoured thermal contraction theory of the mountain building and thus it was obvious that the believers of wrinkle theory should besides discard information technology. 'It is now widely agreed that he (Wegener) handled his instance equally an abet rather than as an impartial scientific observer, actualization to ignore evidences unfavourable to his ideas and misconstrue other evidences in harmony with the theory'.
The critics of Wegener's continental drift theory autumn in two wide categories e.g.:
(i) The critics and writers who always attempted to search errors and discrepancies in Wegener'south original synthesis and
(two) The scientists who attempted to modify, overstate and correct the original theory of Wegener while retaining its basic tenet.
The post-obit flaws and defects have been pointed out past dissimilar scientists in Wegener's theory of the continental drift:
(1) The forces applied by Wegener (differential gravitational force and the strength of buoyancy and tidal force of the dominicus and the moon) are not sufficient enough to drift the continents so apart. The tidal force as invoked by Wegener to account for the supposed westerly drift of the continents would need to be 10,000 million times as powerful as it is at present to produce the required effects, and, if it had such a value, information technology would stop the earth'due south rotation completely in a year'.
Similarly, the differential gravitational force and the forcefulness of buoyancy are besides non adequate to cause equator ward movement of the continents, instead the force, if and then enormous, might take acquired the concentration of the continents most the equator.
(2) Wegener has described several contrasting view-points. Initially, sialic masses (continents) were considered by Wegener every bit freely floating over 'sima' without any friction offered by 'sima' but in later part of his theory he has described forceful resistance of offered by 'sima' in the gratis movement of sialic continents to explain the origin of mountains along the frontal edges of floating continents.
Moreover, 'information technology is difficult to prove how the sial blocks, in their passage through the sima, would crumple at their frontal edges and Produce Mountains'. According to Willis no compression could be possible to course the Rockies and the Andes if the 'sima' is more rigid than the 'sial'. Bowie has maintained that sima has no strength to crumple sial to form mountains.
(3) Both the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean cannot be completely refitted. Thus, the concept of juxtaposition' or 'jig-saw fit' cannot be validated.
(4) Wegener has not elaborated the direction and chronological sequence of the deportation of the continents. He did non depict the situations of pre- carboniferous times. Many questions remain unanswered such as, what kept Pangaea together till its disruption in mesozoic era? Why did the procedure of continental migrate non start before mesozoic era? Etc.
Some writers argue that 'it is non a fair criticism to say that whatsoever pre-carboniferous mountain building cannot be explained on Wegener'south hypothesis just because he does non develop his scheme in earlier geological times'.
It may be concluded that 'even if all the thing of his theory is wrong, geologists and others can but remember that it is largely to him that nosotros owe our more than recent views on globe tectonics'.
Though most signal of Wegener's theory was rejected only its central theme of horizontal displacement was retained. In fact, the postulation of plate tectonic theory subsequently 1960 is the result of this continental drift theory of Wegener. Wegener is, thus, given credit to take started thinking in this precarious field.
Wegener's Hypothesis Of Continental Drift,
Source: https://www.geographynotes.com/theories/continental-drift-theory-of-wegener-geography/2087
Posted by: flowersarkly1973.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Wegener's Hypothesis Of Continental Drift"
Post a Comment